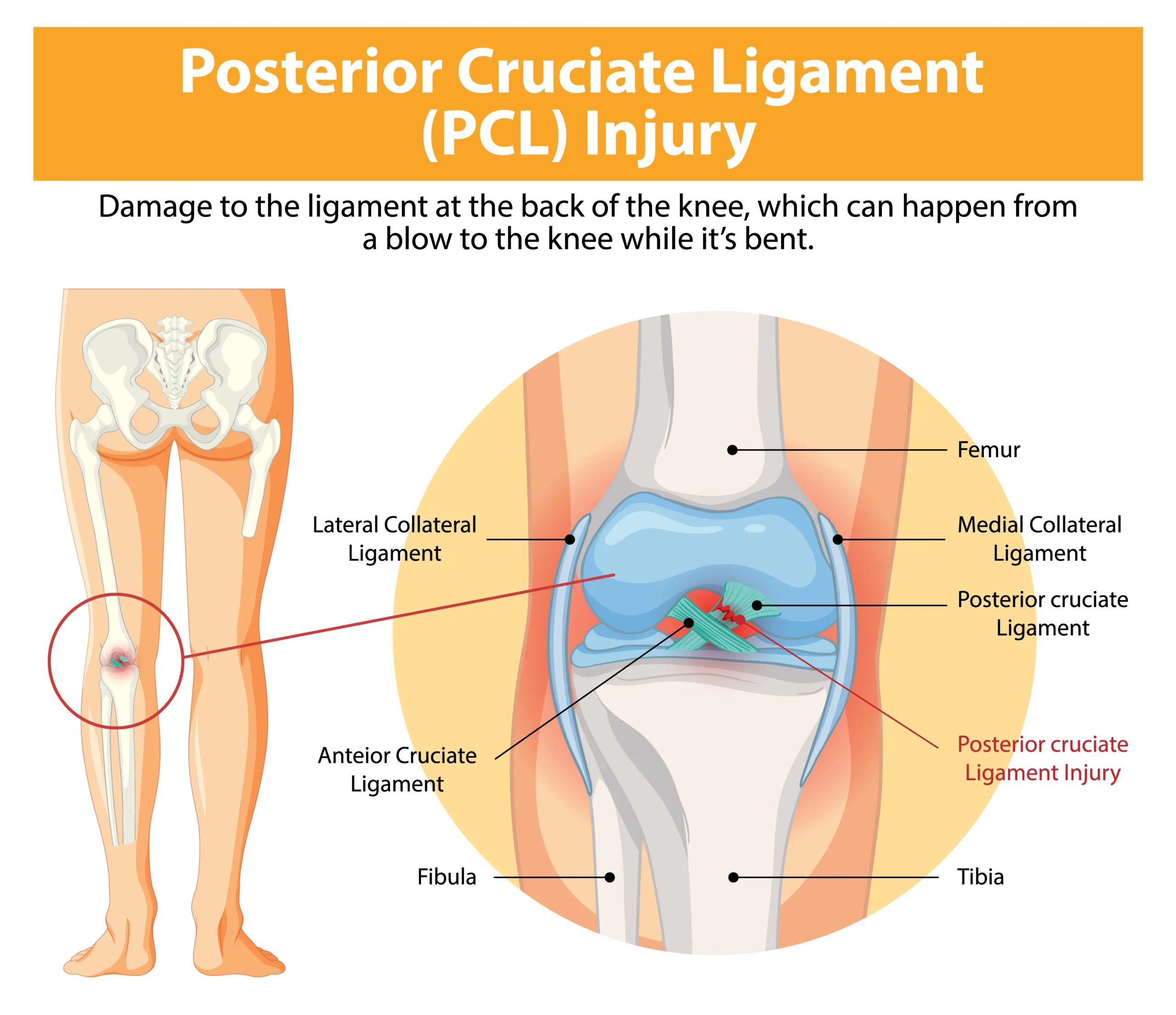
What’s is PCL
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a important ligament within the knee joint . It is located at the back of the knee.PCL is tough bands of tissue similar to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) , connects the thigh bone (femur) to your shin bone (tibia). Although it is larger and stronger than the ACL, but PCL can also be torn.
Function of PCL
The PCL functions as one of the main stabilisers of the knee joint.
Primarily to resist excessive backward movements of the tibia (leg bone) on the femur (thigh bone).
PCL also acts as a secondary stabiliser of the knee preventing excessive rotation specifically between 90° and 120° of knee flexion
PCL Tear Symptoms:
- Instability – Your knee might feel loose, as if it’s going to give way.
- Having Slow movement of the knee due to pain while up-down the stairs.
- Having problems, in turn, and twist the knee.
How to diagnose PCL Injury
- History & Clinical examination by ur doctor
- MRI of knee joint
- Stress x ray of knee joint
Treatment for PCL Injury
Cases that may not require surgery include:
Acute grade I or II injuries when no other knee ligaments are injured
Newly diagnosed chronic injuries that only affect the PCL and aren’t causing symptoms
If there is persistent instability or if more ligaments of the knee are torn, then surgical reconstruction of the ligament is required.
How can PCL reconstruction help?
The rationale for treatment is to stabilise an unstable joint.Joint stabilisation has been shown to decrease meniscal and articular cartilage injury. This should, in turn, decrease the incidence of later osteoarthritic change. It will also allow return to activities that were difficult secondary to joint instability.
PCL Reconstruction Surgery
The reconstruction proceeds along the same lines as an ACL reconstruction
Diagnostic Arthroscopy -it’s a first step of any Arthroscopic surgery like ACL Reconstruction.This means I look inside the joint with a scope using small punctures and very small delicate instrumentation. I look carefully at the injured PCL & determine whether it is torn. An Other associated injuries like meniscus tear & cartilage damage can be deal this time.
Graft harvesting
All knee ligament reconstructions require a graft. Hamstrings /peroneus longus are the preferred graft choice for a PCL reconstruction as well
The graft tissue comes from your own body (autograft)
Usually we harvest Hamstrings /peroneus longus tendons from same operating knee. Preparing the graft & make it four ,five or six strands according to need.
Tunnel placement –with the help of special instruments tunnel is drilled in the tibia (leg bone) & femur (thigh bone) corresponding to the natural locations of the ligament in the knee, according to the size and length of the graft.
Passage of graft & fixation – PCL graft is passed into the tunnels and fixed to the femur and tibia bones with a combination of special buttons, screws and sometimes with staples depending upon the need condition of the bone and graft. In general, most techniques utilise specially designed screws allowing secure immediate fixation of the graft material within bone tunnels drilled into the knee.
These fixation options are discussed with you explaining the pros and cons of each fixation option
Recovery after PCL tear surgery:
Do RICE- Rest, Ice, compression, and Elevation activity daily, it helps to reduce swelling and pain.
Use crutches and braces on an affected knee for first few months to protect the operated knee.
Especially After the surgery patients have to start operated knee flexion gradually.
Don’t drive any vehicle until your doctor not recommend to drive.
Do daily exercises prescribed by your surgeon.

